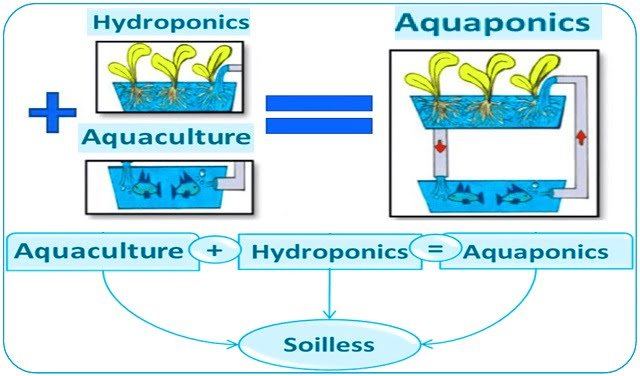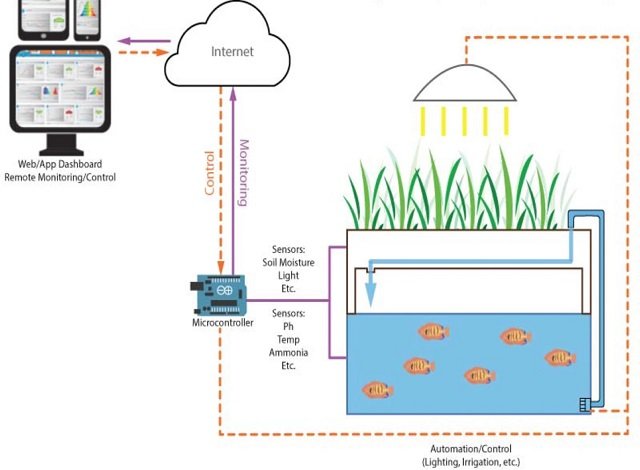
Aquaponic systems are revolutionizing the way we produce food. The integration of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), solar energy, and artificial intelligence (AI) has enabled the development of intelligent aquaponic systems. These systems offer a sustainable and efficient approach to aquaculture and agriculture. However, assessing the performance and effectiveness of these systems remains a complex challenge.
A recent systematic literature review (SLR) conducted by scientists from the Cape Peninsula University of Technology and the University of Pretoria, published in the journal Artificial Intelligence Review, delved into the applications, technologies, and evaluation methods employed in intelligent aquaponics.
Applications and Technologies
The SLR analyzed 105 primary studies from peer-reviewed publications in IEEE Xplore, Scopus, SpringerLink, and Science Direct. The findings revealed that while monitoring and controlling aquaponic systems have been extensively explored (73%), aquaponic predictions have been less studied (27%).
IoT technologies have been used to prototype aquaponic systems and collect data, while machine learning and deep learning have been applied for prediction, anomaly detection, and intelligent decision-making.
Key Technologies Driving Intelligent Aquaponics
- Internet of Things (IoT): This technology enables real-time monitoring of various parameters such as water temperature, pH levels, and nutrient concentrations. By collecting and analyzing data, IoT devices help optimize system performance.
- Machine Learning/Deep Learning: These AI techniques are used to predict system behavior, detect anomalies, and make intelligent decisions. For instance, they can forecast crop yields, optimize resource use, and identify potential issues before they escalate.
The Need for Comprehensive Evaluation
The SLR emphasized the importance of robust evaluation methods for intelligent aquaponic systems. While some studies have incorporated evaluation, many lack a comprehensive approach. Feedback from experts and input from users are essential to assess the usability and practical impact of these systems.
Study Findings
The study analyzed the application areas of aquaponic solutions, focusing on monitoring, control, and prediction. The findings show that:
- Monitoring and Control: Most studies (56%) focused on monitoring and controlling various aquaponic environmental parameters, such as water quality, nutrient levels, temperature, and fish health. Real-time data was used to automate interventions, ensuring optimal growth for plants and fish.
- Prediction: Twenty-seven percent of studies focused on prediction, using historical or external data to forecast specific parameters such as plant and fish growth, water quality, and fruit biomass. Regression and classification techniques were employed for prediction.
- Digital Technologies: IoT technologies were used to create most aquaponic prototype systems (66%), while ML and DL algorithms were applied for prediction, anomaly detection, and intelligent decision-making (17%).
- Strengths and Weaknesses: The analysis revealed strengths in comprehensive system monitoring, technological advancement, diverse applications, and collaboration identification. However, weaknesses included short-term focus, limited environmental variability, and a narrow focus on specific regions.
Future Research Directions
To fully harness the potential of intelligent aquaponics, future research should focus on:
- Long-Term Studies: Conducting long-term experiments to evaluate the performance and sustainability of intelligent aquaponic systems over time.
- Real-World Applications: Testing these systems under diverse environmental conditions to assess their adaptability and robustness.
- Predictive Analytics: Developing advanced predictive models to optimize resource use, enhance yields, and improve overall system efficiency.
- User-Centered Design: Engaging stakeholders and end-users in the design and development process to ensure that systems meet their needs and expectations.
By addressing these areas, researchers can contribute to the advancement of intelligent aquaponics and its widespread adoption as a sustainable food production solution.
Conclusion
The systematic literature review provides new insights into the applications, technologies, and evaluation methods used in intelligent aquaponics. The findings highlight the need for more comprehensive evaluation methods and the importance of addressing the limitations of existing studies.
Stay Always Informed
Join our communities to instantly receive the most important news, reports, and analysis from the aquaculture industry.
Exploring the potential of intelligent aquaponics can unlock new opportunities for sustainable food production and contribute to a future with greater food security.
Open access was funded by the University of Pretoria and Cape Peninsula University of Technology.
Contact
Olawande Daramola
Department of Informatics, University of Pretoria
Pretoria, South Africa
Email: wande.daramola@up.ac.za
Reference (open access)
Anila, M., Daramola, O. Applications, technologies, and evaluation methods in smart aquaponics: a systematic literature review. Artif Intell Rev 58, 25 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-11003-x
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.