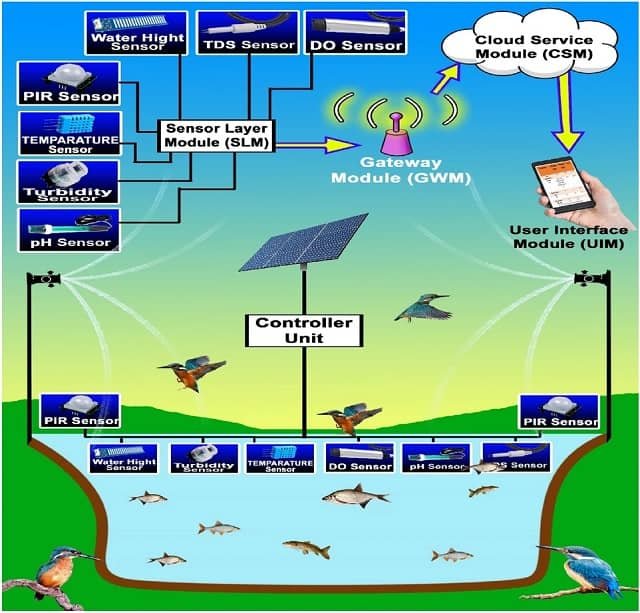
The aquaculture industry is undergoing a transformative shift thanks to the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT). A recent bibliometric analysis published in the journal Applied Food Research by researchers from Széchenyi István University, the University of Carthage, and McGill University sheds light on how IoT technologies are enhancing productivity, sustainability, and resilience in aquaculture.
The role of IoT in aquaculture
IoT refers to a network of interconnected devices, sensors, and systems that collect, transmit, and analyze real-time data. In aquaculture, IoT technologies are used to monitor water quality, automate feeding processes, and manage fish health, among other applications. These innovations are crucial for addressing the industry’s unique challenges, such as maintaining optimal water conditions, preventing disease outbreaks, and improving resource efficiency.
According to the study, IoT-enabled devices such as water quality sensors, automatic feeders, underwater cameras, and autonomous drones are revolutionizing aquaculture operations. These tools provide real-time data on critical parameters such as temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH, salinity, and ammonia levels. This data enables aquaculture operators to make informed decisions that mitigate risks, optimize resource use, and enhance productivity.
Key IoT applications in aquaculture
Water quality monitoring
Maintaining water quality is essential for the health and growth of aquatic species. IoT sensors allow continuous monitoring of water parameters, generating real-time alerts that enable proactive interventions, such as water recirculation or aeration, before conditions deteriorate.
Feeding management
Feeding costs account for 50% to 70% of aquaculture operational expenses, and inefficient feeding practices can lead to waste and environmental pollution. IoT-based automated feeding systems use data on fish behavior, water temperature, and other environmental conditions to optimize feeding schedules and quantities, reducing waste and improving growth rates.
Disease prevention
Disease outbreaks can cause significant economic losses in aquaculture. IoT-based health monitoring systems analyze behavioral and environmental data to detect early signs of disease, allowing timely treatments and reducing the risk of widespread outbreaks.
Labor productivity
Traditional aquaculture practices rely heavily on manual labor for supervision and maintenance. IoT technologies automate routine tasks, reducing the need for manual inspections and minimizing human error. This is particularly beneficial in regions with labor shortages or high labor costs.
Emerging trends and research gaps
The bibliometric analysis identified several emerging trends in IoT and aquaculture research, including the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive analysis, the use of blockchain for traceability, and the development of energy-efficient IoT devices. However, the study also highlighted several research gaps that need to be addressed:
- Interoperability: Ensuring seamless communication and data exchange between different IoT devices and platforms remains a challenge.
- Data Security and Privacy: Since IoT systems collect and transmit large amounts of data, ensuring data security and privacy is crucial.
- Scalability: Many IoT solutions are designed for large-scale operations, leaving small-scale and resource-limited aquaculture systems underserved.
Geographical and thematic perspectives
The study revealed that countries such as India, Indonesia, and China are leading IoT research in aquaculture, driven by their significant contributions to global aquaculture production. These countries heavily invest in digital and technological initiatives to enhance food production and sustainability.
Stay Always Informed
Join our communities to instantly receive the most important news, reports, and analysis from the aquaculture industry.
The thematic analysis of the research landscape identified four main clusters:
- Smart and Precision Aquaculture Systems: Focused on integrating IoT with AI, machine learning, and big data for precision farming and environmental sustainability.
- Integrated Aquaponics and Smart Farming Technologies: Exploring the convergence of aquaculture and agriculture through IoT-based systems.
- Water Quality and Health Monitoring: Emphasizing the use of sensors and AI models to monitor critical water parameters and fish health.
- Intelligent Aquaculture Monitoring and Forecasting Systems: Leveraging IoT, machine learning, and cloud computing for real-time monitoring and predictive management.
Future directions
The study emphasizes the need for future research to focus on enhancing IoT integration in aquaculture, particularly the fusion of real-time data collection with predictive analytics. Additionally, addressing ethical considerations such as data privacy and the impact of automation on employment is essential for the sustainable adoption of IoT technologies.
Conclusion
The integration of IoT in aquaculture represents a significant shift from labor-intensive traditional practices to data-driven automated systems that enhance productivity and sustainability.
By leveraging IoT, aquaculture operators can optimize resource use, improve fish health, and reduce environmental impact, paving the way for a more resilient and sustainable future for the industry.
Reference (open access)
Rejeb, A., Rejeb, K., & Keogh, J. G. (2025). The nexus of IoT and aquaculture: A bibliometric analysis. Applied Food Research, 100838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.afres.2025.100838
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.







