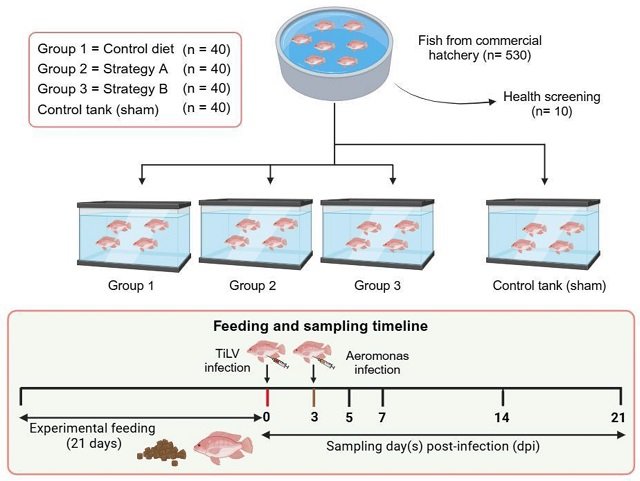
One of the most devastating combinations is the co-infection of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) and Aeromonas hydrophila. A recent study published in the MDPI journal has revealed promising dietary strategies to enhance tilapia resistance to these infections.
Researchers from Kasetsart University, ADISSEO France S.A.S., and the Chulabhorn Research Institute explored the effects of two different dietary supplement strategies on hybrid red tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) infected with Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) and Aeromonas hydrophila. The results show that these dietary supplements can significantly boost the fish’s immune system and improve their survival against these pathogens.
The Double Blow: A Lethal Combination
The synergy between these pathogens can exacerbate their impact, leading to higher mortality rates and significant economic losses for the aquaculture industry.
For instance, the deadly combination of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) and Aeromonas hydrophila has been linked to severe outbreaks in tilapia populations. Co-infected fish show increased susceptibility, worse clinical signs, and higher mortality rates compared to those infected with a single pathogen.
Emerging Strategies to Combat Diseases
- Feed Additives: Incorporating substances like phytogenic essential oils, acidifiers, organic acids, algae, and cyanobacteria into fish feed can enhance immune function and reduce susceptibility to infections.
- Probiotics: Beneficial bacteria, such as Bacillus spp. and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, can strengthen gut microbiota and reinforce the immune system.
The Power of Nutrition
Researchers investigated the effects of two different dietary supplement strategies on hybrid red tilapia.
- Strategy A: A mix of organic acids and a digestive enhancer based on lysophospholipids.
- Strategy B: A combination of organic acids, natural immunostimulants, and essential nutrients.
The fish were exposed to both TiLV and A. hydrophila and fed with one of these supplemented diets or a standard control diet.
Key Findings
- Improved Survival: Fish fed with Strategy A or B showed significantly lower mortality rates compared to the control group. However, Strategy B proved particularly effective, resulting in the lowest mortality rate.
- Enhanced Immune Response: Fish fed with Strategy B displayed a robust immune response, characterized by lower inflammatory gene expression and reduced pathological changes in vital organs.
- Gut Protection: While Strategy A did not significantly impact the immune response, it showed protective effects on the intestinal tract, potentially reducing pathogen entry.
Implications for Tilapia Farming
These findings offer valuable insights for tilapia farmers. By incorporating these dietary strategies into their feeding practices, they can strengthen their fish’s immune systems and protect them from the devastating effects of co-infections. This, in turn, can lead to healthier fish populations, increased production, and improved economic sustainability for the aquaculture industry.
Conclusion
This study highlights the potential of feed additives, particularly Strategy B, to reduce the impact of viral and bacterial co-infections and improve outcomes in tilapia farming. The results suggest that dietary supplements can play a crucial role in strengthening tilapia’s immune systems and enhancing their survival against pathogens.
“Specifically, Strategy B, which contained organic acids and natural immunostimulants, effectively reduced mortality and modulated the fish’s immune response, while Strategy A, which included organic acids and lysophospholipids, had significant protective effects on the fish’s intestines,” the scientists reported.
Stay Always Informed
Join our communities to instantly receive the most important news, reports, and analysis from the aquaculture industry.
As the global tilapia aquaculture industry continues to face the challenges of disease outbreaks, developing effective feed additives like Strategy B could provide valuable support for farmers and help ensure the long-term sustainability of the industry.
The study was funded by the Office of the Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation, and Thailand Science Research and Innovation through the Kasetsart University Reinventing University Program 2022.
Reference (open access)
Mohamad, A., Yamkasem, J., Paimeeka, S., Khemthong, M., Lertwanakarn, T., Setthawong, P., G., W., Isern Subich, M. M., & Surachetpong, W. (2024). Efficacy of Feed Additives on Immune Modulation and Disease Resistance in Tilapia in Coinfection Model with Tilapia Lake Virus and Aeromonas hydrophila. Biology, 13(11), 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13110938
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.







