
Washington – A new report from the World Bank estimates that ten emerging global seaweed markets have the potential to grow up to $11.8 billion by 2030.
This monetary value comes alongside the capacity of seaweed to absorb carbon, maintain marine biodiversity, provide employment for women, and unlock value chains.
The “Global Seaweed New and Emerging Markets Report 2023” analyzes business opportunities for new high-growth seaweed market applications. The report provides insights for entrepreneurs, investors, and policymakers to ensure that the seaweed sector reaches its potential now and in the future.
Uses of Seaweed
While macroalgae have been cultivated for decades in many parts of Asia, there is growing interest in producing a wide range of seaweed species worldwide.
Seaweed cultivation, with its ability to absorb carbon, maintain marine biodiversity, provide employment for women, and unlock value chains, demonstrates how development, climate, and nature work together to generate value and improve communities.
Currently, most cultivated seaweed is used for direct human consumption or as fresh feed in aquaculture. In the future, seaweed products could replace fossil fuels in sectors such as textiles and plastics, sequester carbon, and generate income for vulnerable coastal communities.
There are enormous growth opportunities in many regions, as the current market is dominated by a few Asian countries that produce 98% of cultivated seaweed.
“The growth of seaweed cultivation worldwide will depend on the exchange of technology and knowledge among policymakers, financial institutions, the scientific community, the private sector, producers, and processors, leaving no one behind. With women predominantly engaged in seaweed cultivation, the stage is set to catalyze a true global ‘she-weed’ revolution,” said Valerie Hickey, World Bank’s Global Director for Environment, Natural Resources, and Blue Economy.
The report focuses on 10 relatively new and emerging seaweed applications with the greatest market opportunities outside established sectors.
Commercial Value Growth
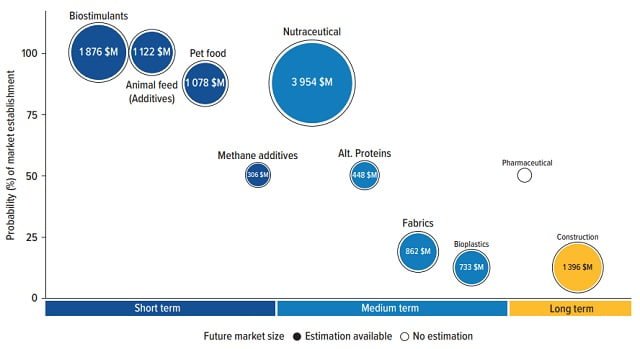
In the short term, the most promising new markets are projected to reach $4.4 billion by 2030, including bio-stimulants, animal feed, pet food, and methane-reducing additives.
Mid-term opportunities include nutritional supplements, alternative proteins, bioplastics, and fabrics, potentially reaching a value of $6 billion. Long-term emerging markets could reach $1.4 billion for pharmaceuticals and construction materials, but they face significant regulatory challenges and high product development costs.
“Seaweed cultivation demonstrates how development, climate, and nature work together to generate value and improve communities. Seaweed cultivation will be a source of nutritional security as well as an alternative to synthetic fertilizers,” said Martien van Nieuwkoop, World Bank’s Global Director for Agriculture and Food. “The World Bank is committed to helping countries transform food systems for better outcomes for people, the planet, and economies.”
Short-Term Markets: Pre-2025
In the short term, bio-stimulants, animal feed additives, and pet food are the most promising markets for seaweed, with a projected value of $4.4 billion by 2030. Macroalgae-based products in these high-growth markets show competitive pricing and value propositions.
Animal feed additives reduce dependence on synthetic products and enhance animal productivity by reducing feed conversion rates. Methane-reducing additives represent a completely new market, but significant technological and regulatory challenges still persist.
Mid-Term Markets: 2024 – 2028
Nutraceuticals offer a high-value mid-term market, but the potential for regulatory constraints to hinder market development is projected to reach $6.0 billion by 2030.
Alternative proteins, renewable biomass-based bioplastics, and manufacturing are emerging as business opportunities in the mid-term. Due to significant production costs, pricing, and functionality challenges, these markets will require substantial improvements in seaweed cost and availability.
Long-Term Emerging Markets: Post-2028
Pharmaceuticals offer a long-term market opportunity, but significant regulatory challenges and high product development costs exist.
Construction, including construction materials, may present a long-term emerging market projected to reach $1,400 million by 2030, but more likely as a niche application or through waste valorization in seaweed processing.
Seaweed Industry Challenges
To fully harness the potential of the seaweed market, the industry must overcome several key issues. The greatest challenge is the availability of seaweed itself, due to limitations in volume, consistency, and supply quality. As more seaweed applications develop, regulatory and pricing barriers may also arise.
Despite these challenges, the climate and environmental benefits of seaweed cultivation will help drive the growth of potential emerging markets. As interest in “green” products continues to rise, many product developers have expressed confidence in sustainability premiums for generating profits.
At a time when global resources are increasingly strained, it is particularly important for the world to make the most of resources like seaweed, which can regenerate quickly and potentially help restore ecosystems.
Conclusion
As the study concludes: “The seaweed sector has a clear growth potential beyond its current markets and can help shape a world free of poverty on a habitable planet.”
It also reports that enhanced seaweed production and improved value chains can contribute to achieving at least nine of the United Nations’ 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). For example, seaweed cultivation can absorb carbon, maintain marine biodiversity, and provide employment for women.
Reference (open access)
World Bank. 2023. Global Seaweed: New and Emerging Markets Report, 2023. © Washington, DC: World Bank. http://hdl.handle.net/10986/40187

