Predicting export prices is important in the aquaculture industry, as it helps producers determine their production strategies.
Competition in the world market is considered to be an important factor, one that significantly influences the price.
Researchers from Can Tho University and Hokkaido University used machine learning to predict export price trends for Vietnamese shrimp based on competitive information from the top six exporters (China, India, Indonesia, Thailand, Ecuador, and Chile). ) who, like Vietnam, export shrimp to the US.
The study provides a new approach to making reliable Vietnamese shrimp price predictions based on competitor data rather than just Vietnamese data.
Computer models
The application of computerized techniques to improve management, predict diseases or analyze market trends is widely used. For example, an expert system and digital image processing tools were used to diagnose shrimp diseases.
Machine learning has been used to predict the presence of shrimp diseases and create applications for aquaculture; Also to forecast sales.
Price prediction is important for fishery and aquaculture exports because it helps determine global market trends and increases the quality of seafood products.
Although machine learning algorithms are useful for making predictions, they depend on a reliable database.
Databases used
The researchers used the databases of the US Department of Agriculture (USDA), the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), and the World Trade Organization (WTO), in the period from May 1995 to May 2019.
The seven leading exporters of frozen shrimp products for the US market (China, Thailand, India, Indonesia, Ecuador, Chile, and Vietnam) were included in the database.
The exporting countries were direct competitors in the US market; therefore, an increase in the export price of any of the listed countries may change the demand curve for shrimp products imported into the US market.
The technique of “super learner”
A technique known as “super learner”, which combines 10 simple algorithms, was used to make the predictions in selected base periods (3, 6, 9, and 12 months).
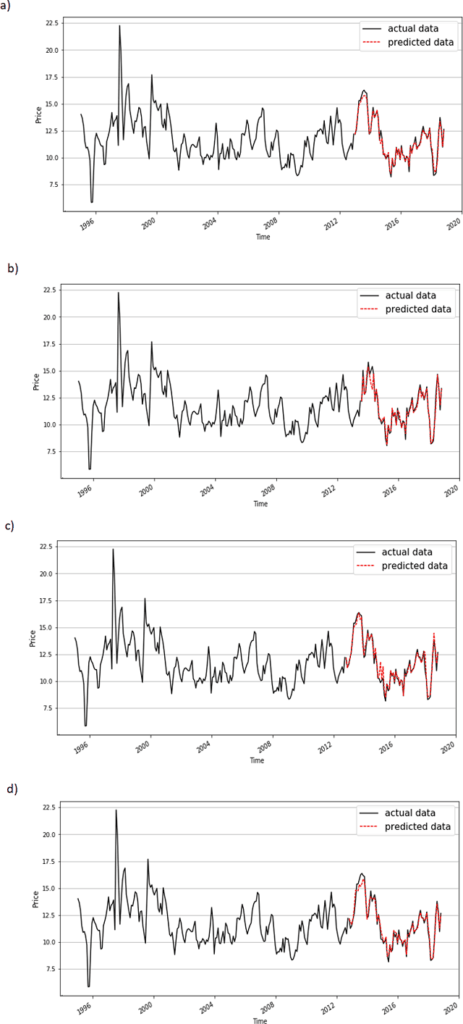
To interpret the prediction, the researchers used the SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) method to determine how each predictor influences the export price and then suggest solutions to develop the Vietnamese shrimp industry.
The researchers found that the super learner returned results across all base periods that were more approximate and stable than any other candidate algorithm.
According to the study, the SHAP analysis results highlight that the price difference with India, WHO membership, the price difference with Thailand, the price difference with China, the Early Mortality Syndrome outbreak and the price difference price with Ecuador had the greatest impacts on the prediction of Vietnamese shrimp prices.
“Although other factors, including Aquaculture Steward Council, Global GAP, Safe Quality Food, and HACCP certificates, had less impact on the predictive model, they also impact the export price of Vietnam and other countries in terms of ensuring the health, traceability, and risk of disease” report the researchers.
According to the study, Vietnam is likely to get better prices for its shrimp products if it fully implements shrimp export safety certificates, which can give it a competitive advantage over other producing countries in the international market.
Conclusion
“The prices of exports from India, Thailand, and China highlight the advantage of being members of the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the disadvantage of the prevalence of shrimp diseases in Vietnam, which had a significant impact on the export price of Vietnamese shrimp”, they conclude.
Contact
Nguyen Minh Khiem
College of Information and Communication Technology,
Can Tho University,
Can Tho, Vietnam
nmkhiem@cit.ctu.edu.vn
Reference (open access)
Khiem NM, Takahashi Y, Yasuma H, Dong KTP, Hai TN, Kimura N (2022) A novel machine learning approach to predict the export price of seafood products based on competitive information: The case of the export of Vietnamese shrimp to the US market. PLoS ONE 17(9): e0275290. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0275290
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.
