The world faces a pressing challenge: ensuring food security for a growing population while protecting our planet’s resources. Conventional agricultural practices are exerting pressure on our ecosystems, and the current linear economic model does not ensure sustainable food production and consumption.
But what if there was a way to cultivate food sustainably, combat hunger, and empower communities simultaneously?
Fortunately, innovative solutions like aquaponics offer a sustainable and impactful approach to achieving Zero Hunger, as outlined in the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda.
An article published by scientists from the Autonomous University of Querétaro and the University of Veracruz explores how aquaponics, a nature-inspired agricultural technique, can contribute to Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG 2): Zero Hunger in Mexico. However, their findings can be extrapolated to other nations.
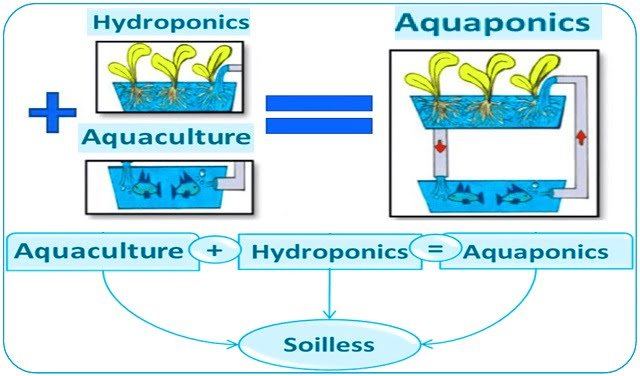
The Opportunity: Aquaponics
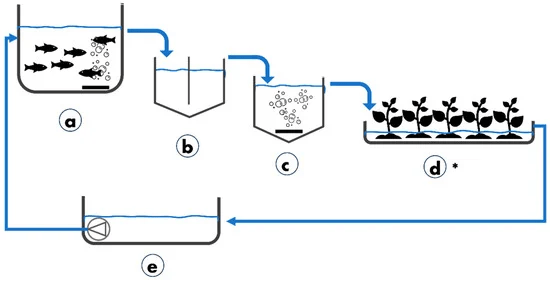
Aquaponics provides a sustainable solution by mimicking natural ecosystems and using “organically enriched water” from aquaculture for plant growth.
This innovative technology has the potential to:
- Increase food production: Aquaponics can produce more food per unit of area and water compared to traditional agriculture.
- Improve nutrition: The system can produce diverse and nutrient-rich fish and vegetables.
- Economic benefits: Local food production can create jobs, empower communities, and reduce dependence on external food sources.
- Environmental sustainability: Aquaponics conserves water, reduces waste, and minimizes environmental impact.
- Empower communities: Scalable from small installations to large-scale systems, making it accessible to various stakeholders, including small farmers, women, and rural communities.
Zero Hunger Goal with Aquaponics
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development outlines a roadmap for a better future, with Goal 2: Zero Hunger at its core. This ambitious goal aims to end hunger, achieve food security, improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture.
This document highlights how aquaponics can directly address the first three targets of Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG 2):
Target 2.1: End hunger with nutrient-rich rewards
Aquaponics is not just about growing food; it’s about cultivating nutritious food. The symbiotic relationship between fish and plants in an aquaponic system creates a natural fertilizer rich in organic nutrients that nourish crops. Studies have shown that aquaponic plants have higher levels of vitamins, minerals, and bioactive molecules compared to conventionally grown crops, making them more effective in combating hunger and malnutrition.
Stay Always Informed
Join our communities to instantly receive the most important news, reports, and analysis from the aquaculture industry.
Target 2.2: Tackling malnutrition at the root
Beyond basic caloric intake, aquaponics addresses hidden hunger, and the lack of essential micronutrients that often affect vulnerable populations. The higher nutrient content of aquaponic crops means they provide greater nutritional value, supplying essential vitamins and minerals to combat deficiencies and promote overall health.
Target 2.3: Empowering small farmers, a significant impact
The beauty of aquaponics lies in its scalability. Unlike traditional agriculture, which often requires large land areas, aquaponic systems can be adapted to various scales, from rooftop gardens to community farms. This makes it an ideal option for small farmers, women, and rural communities to produce their own food, ensure food security, and generate income.
Unleashing the Potential: Local Action, Global Impact
While aquaponics has immense potential, local support and infrastructure development are crucial for widespread adoption. This includes investing in research, education, and training, creating access to resources and financing, and fostering collaboration among communities, governments, and research institutions. By nurturing a supportive ecosystem, we can unlock the transformative power of aquaponics and cultivate a future where Zero Hunger is no longer a dream but a reality.
Conclusion
Aquaponics has immense potential to address food security challenges in Mexico and around the world, contributing to SDG 2 and fostering a more sustainable and resilient food system. By harnessing its potential, Mexico can pave the way for a future where communities thrive, and our planet flourishes.
Are you ready to be part of the solution? Whether you’re a consumer seeking nutritious food, a farmer exploring sustainable options, or an advocate for food justice, there’s a place for you in the aquaponics movement.
Reference (open access)
Flores-Aguilar, Priscila Sarai, Julieta Sánchez-Velázquez, Humberto Aguirre-Becerra, Guillermo Abraham Peña-Herrejón, Sergio Aurelio Zamora-Castro, and Genaro Martín Soto-Zarazúa. 2024. “Can Aquaponics Be Utilized to Reach Zero Hunger at a Local Level?” Sustainability 16, no. 3: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16031130
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.