In the face of a growing population, diminishing water resources, and a changing climate, the need for sustainable and efficient aquaculture and agriculture practices has never been greater.
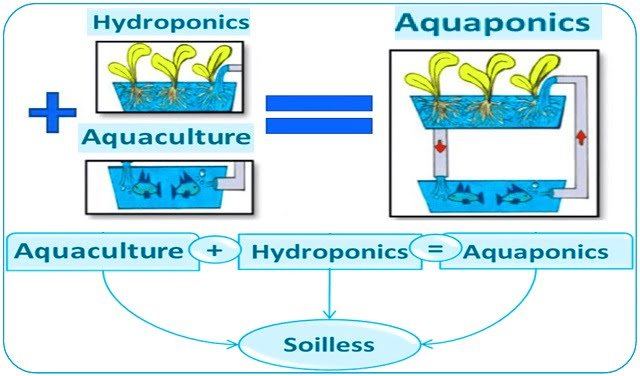
Aquaponics emerges as an opportunity, offering a revolutionary approach that harmonizes aquaculture and hydroponics to create a closed-loop ecosystem thriving on resource efficiency.
A team of researchers from the National Water Research Center (NWRC), Hohai University, Zagazig University, Damietta University, and Hohai University published a detailed scientific review exploring aquaponics as an environmentally friendly solution aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals and food sovereignty, assessing various aspects from system design to automation.
Benefits of Aquaponics
The advantages of aquaponics extend beyond water conservation. This innovative method boasts a variety of benefits, including:
- High-Quality Yields: By providing easily accessible nutrients to plants, aquaponics can yield abundant organic vegetables and fruits.
- Sustainable Protein Sources: Aquaponics systems, integrating hydroponics and aquaculture, become a sustainable source of plant and animal-based proteins.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: The closed-loop system minimizes reliance on chemical fertilizers and pesticides, contributing to a healthier environment for both plants and fish.
- Adaptability: Aquaponics can be adapted to various environments, including urban settings, offering a potential solution for food security in resource-limited areas.
Water Use Optimization
At the core of aquaponics is water efficiency. The closed-loop system design minimizes water needs, resulting in significant water savings compared to traditional agricultural production systems. This efficiency is further enhanced by:
- Precise Control: Sensor-based systems can monitor and adjust water flow, ensuring plants receive the right amount of water for optimal growth.
- Nutrient Recycling: Fish waste nutrients are easily absorbed by plants, minimizing the need for external fertilizers and reducing water pollution.
Alignment with SDGs and Food Sovereignty
Aquaponics is not just a peculiar farming method; it’s a response to some of our planet’s most pressing challenges. It aligns perfectly with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 2 for Zero Hunger and SDG 6 for Clean Water and Sanitation. Producing high-quality food with minimal water and resource usage, it empowers communities to achieve food sovereignty and break free from the often unsustainable practices of traditional agriculture and aquaculture.
Aquaponics is no longer an exclusive concept. Initiated by the University of the Virgin Islands, it is now taking root in Europe, with Spain, Denmark, Italy, and Germany leading the way. Asia and Africa are also recognizing its potential, with Egypt exploring its capabilities for organic food production in deserts and coastal regions.
Harnessing Technology for the Future
The future of aquaponics is brimming with possibilities. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) have immense potential for:
- Automated Management: AI-driven systems can analyze sensor data and automatically adjust irrigation, fertilization, and other parameters for optimal growth.
- Remote Monitoring: IoT-enabled systems can enable real-time monitoring and control of aquaponics systems from anywhere, making them ideal for urban environments or remote locations.
- Precision Aquaculture: Data-driven information can be used to customize aquaponics systems for specific crop varieties and environmental conditions, further optimizing yields and resource efficiency.
While integrating Industry 4.0 technologies such as artificial intelligence and automation holds great promise, it also poses challenges in terms of complexity and cost.
From Niche to Mainstream
While aquaponics holds immense promise, it faces certain challenges. Scaling up systems for commercial production requires more research and development. Adapting aquaponics to diverse environmental conditions and developing effective strategies for urban integration are also crucial areas for future research.
Despite its potential, aquaponics still faces some obstacles:
- Organic Certification: Obtaining organic certification for aquaponics systems can be complex and costly, hindering wider adoption.
- Legislative Recognition: Lack of clear regulations and legal frameworks around aquaponics can create uncertainty for investors and farmers.
- Scaling: Moving from small-scale facilities to large-scale commercial production demands innovation and cost-effective solutions.
- Water Quality Management: Maintaining optimal water quality is crucial for the health of fish and plants. Advanced monitoring and filtration systems are essential.
By addressing these challenges and harnessing the power of technology, aquaponics can truly transform the future of food production.
Conclusion
The innovative approach of aquaponics has the potential to enhance food security, promote sustainable development, and empower communities worldwide.
By leveraging the power of research, innovation, and local adaptation, we can unlock the true potential of aquaponics to revolutionize sustainable food production globally. Aquaponic systems offer a resilient and efficient solution to grow the food we need while protecting the valuable resources we depend on.
The study was funded by the Jiangsu Funding Program for Excellent Postdoctoral Talent and the Foreign Youth Talent Project.
Reference (open access)
Ibrahim, Lubna A., Hiba Shaghaleh, Gamal Mohamed El-Kassar, Mohamed Abu-Hashim, Elsayed Ahmed Elsadek, and Yousef Alhaj Hamoud. 2023. “Aquaponics: A Sustainable Path to Food Sovereignty and Enhanced Water Use Efficiency” Water 15, no. 24: 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15244310
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.
