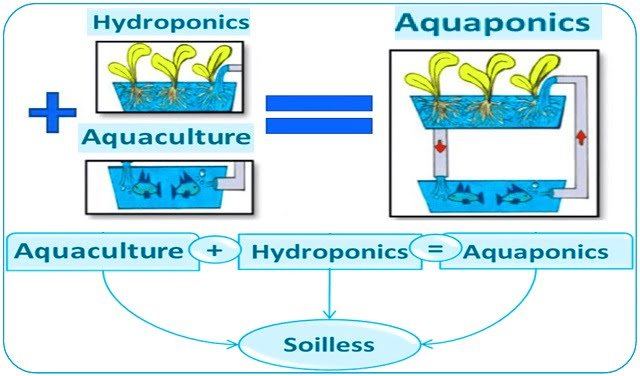
In the dynamic realm of sustainably producing food, aquaponics emerges as an innovative fusion of aquaculture and hydroponics. This symbiotic system integrates microorganisms, fish, and plants in a shared aquatic environment.
The success of aquaponics hinges on bacteria orchestrating crucial processes like nitrification and nutrient extraction. However, this intricate balance also harbors potentially hazardous microorganisms from various origins, raising concerns about risks to human health.
This article explores the delicate equilibrium within aquaponic systems, shedding light on pathogenic threats, their origins, and innovative control methods.
Microbial Diversity: Beneficial and Potentially Hazardous
Aquaponics relies on a delicate interaction of microorganisms. Beneficial bacteria are essential for processes like nitrification and nutrient extraction from fish waste. However, alongside these allies, potentially hazardous microorganisms of fish, human, and plant origin exist. Balancing this microbial diversity is crucial to ensure the safety of both fish and plants cultivated in aquaponic systems.
Assessment of Risks to Human Health
Understanding the presence and potential threats of human pathogens in aquaponics is fundamental. Literature analysis reveals that while aquaponic bacteria and yeasts primarily pose risks to fish and humans, plants are less susceptible. Conversely, molds can be pathogenic to humans, plants, and fish. Establishing the pathways through which human pathogens enter aquaponic systems is essential for designing effective control measures.
The study provides a list of microorganisms present in aquaponic systems with the potential to affect human health.
Risk Mitigation: Hygiene
The key to minimizing risks to human health lies in the rigorous application of proper hygiene practices. Aquaponic pathogens enter the water when hygiene protocols are neglected. A literature review emphasizes that meeting and maintaining these hygiene standards transform aquaponic systems into a safe haven for cultivating fish and plants suitable for human consumption.
“UV disinfection in soilless production systems involves exposing tank water to light in the germicidal range of approximately 225 to 312 nm. These lights typically disinfect effluent water from the fish tank but can also be used to disinfect incoming water. The mechanisms of pathogen inactivation involve damage to DNA and mRNA, with bacteria being the most susceptible to this damage,” the authors report.
Stay Always Informed
Join our communities to instantly receive the most important news, reports, and analysis from the aquaculture industry.
Additionally, they highlight that thermal treatment is highly effective against pathogens, achieving denaturation of their proteins resulting in a 90-99.9% reduction in the initial microbial population. However, to suppress all types of pathogens, it is necessary to reach a temperature of 95 °C for at least 10 s.
Challenges in Disease Control: Antibiotic Dilemma
While conventional disease control methods include physical and chemical measures, antibiotic treatment poses challenges. Many aquaponic pathogens feature on the World Health Organization’s list of drug-resistant bacteria, demanding urgent antibiotic alternatives. Conventional approaches, if misapplied, risk harm to humans, fish, plants, and beneficial microorganisms.
Innovative Alternatives: Biocontrol
In the quest for safer disease control, innovative alternatives emerge. Biological control, utilizing antagonistic microorganisms, shows promise. Phytotherapy, bacteriophage therapy, and nanomedicine present intriguing avenues. These alternatives, avoiding the pitfalls associated with traditional methods, herald a new era in sustainable aquaponics.
Conclusion
As the world seeks sustainable aquaculture practices, aquaponics stands out for its potential to harmonize the cultivation of fish and plants. The key lies not only in understanding microbial complexities but also in implementing strict hygiene practices.
“It is worth noting that many of the aquaponic pathogens are listed on the WHO list of drug-resistant bacteria for which new antibiotics are urgently needed,” the study authors report.
Innovative alternatives to conventional disease control methods pave the way for a future where aquaponics contributes to both environmental sustainability and the production of healthy, safe-to-consume food. By embracing these advances, we can cultivate a future where the delicate balance of aquaponics thrives, ensuring a bountiful harvest without compromising human health.
The study was funded by the Bulgarian Ministry of Education and Science (MES) as part of the Bulgarian National Recovery and Resilience Plan, Component “Innovative Bulgaria,” and the project “Development of research and innovation at Trakia University in service of health and sustainable well-being.”
Reference (open access)
Dinev, Toncho, Katya Velichkova, Antoniya Stoyanova, and Ivaylo Sirakov. 2023. “Microbial Pathogens in Aquaponics Potentially Hazardous for Human Health” Microorganisms 11, no. 12: 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122824
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.