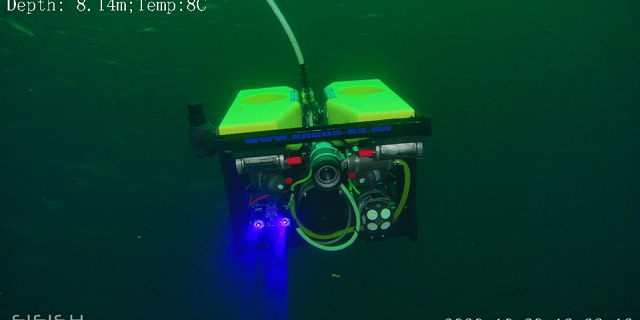
Imagine automated underwater drones patrolling fish farms, monitoring water quality, and detecting diseases before they spread. Robots that accurately distribute feed, optimize growth, and reduce waste. Sounds futuristic, doesn’t it? But this vision is quickly becoming a reality thanks to the exciting integration of robotics in aquaculture.
As the increasing demand for seafood products clashes with challenges such as overfishing and climate change, it is crucial to ensure a sustainable supply of this vital source of protein. Traditional aquaculture methods often face limitations in terms of efficiency, environmental impact, and disease control. This is where robots come in, offering a transformative approach to sustainable seafood production.
A team of scientists from the University of Horticulture and Forestry, Colleges of Agricultural Engineering, and Era University published a study exploring the integration of robotics into aquaculture practices to achieve sustainable production of fish and seafood.
Robotic Innovations in the Aquaculture Industry
According to scientists, the integration of robotic technologies in aquaculture has heralded the beginning of a new era of precision, efficiency, and sustainability. “These innovations encompass various aspects of aquaculture operations, from monitoring and feeding to disease detection and environmental control,” they report.
The use of robotics in aquaculture will enable the optimization of production processes, minimize resource waste, and monitor the health of aquaculture species.
Benefits of Robotics
According to the study, the main benefits of using robots in aquaculture include:
- Enhanced monitoring: Robotic systems equipped with sensors can continuously monitor water quality, fish health, and environmental parameters, providing real-time data for informed decision-making. They can also prevent fish escapes.
- Improved maintenance activities: Robots can perform a range of maintenance operations in aquaculture facilities, such as repairing cages in the salmon industry.
- Precision feeding: Automated feeders ensure optimal food distribution, minimizing waste and maximizing fish growth while reducing nutrient pollution.
- Early disease detection: AI-driven robots can identify disease outbreaks more quickly and accurately, allowing for swift intervention to prevent widespread infections.
- Habitat management: Submarine drones can map and assess aquaculture environments, optimize population densities, and even eliminate harmful algae blooms.
Case Studies of Robotic Use
The study presents some case studies of robotic use in the aquaculture industry. These studies analyze the use of robots in feeding and monitoring salmon and shrimp; the use of robotic arms for oyster cultivation; inspection of cages by remotely operated vehicles (ROVs); macroalgae harvesting, among others.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
While the potential is immense, there are obstacles to overcome. The initial investment cost of robotics can be high, and it may be necessary to adapt existing agricultural infrastructure. Additionally, it is crucial to ensure the ethical treatment of farmed fish and the responsible integration of technology into the aquaculture ecosystem.
Despite these challenges, the future of aquaculture appears increasingly robotic. Ongoing research and development are reducing costs, improving robot capabilities, and encouraging responsible implementation. With advancements in automation, data analysis, and artificial intelligence, robot-assisted aquaculture promises a more sustainable, efficient, and secure seafood supply for future generations.
Conclusion
“The study highlights the versatility of robotic applications in aquaculture, spanning various species, production methods, and geographic contexts. By effectively addressing specific challenges, these innovations contribute to increased efficiency and reduced environmental impact,” conclude the researchers.
It is important to note that robots are part of a series of disruptive technologies linked to digital twins and artificial intelligence that are being applied in the aquaculture industry. Likewise, it is essential to understand the impact that these technologies can have on the welfare of aquaculture species.
Reference (open access)
Lal , S., Ahirwar , S. B., Kanojia , S., Rai , S., Vidhya C. S., Gupta , S., Nautiyal , C. T., & Nautiyal , P. (2024). Robot-assisted Aquaculture and Sustainable Seafood Production for Enhanced Food Security. International Journal of Environment and Climate Change, 14(2), 215–220. https://doi.org/10.9734/ijecc/2024/v14i23938
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.
