Phytochemicals can boost growth performance, non-specific immune responses, and antioxidant capacity in fish and shrimp. Previous studies have shown that phytosterols can supplement the cholesterol requirements of Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei).
A study aimed to evaluate the impact of Achyranthes aspera herb extract, with a focus on its phytosterol content (200 mg/kg), when incorporated into the diet of Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei).
Conducted by scientists from Jeju National University and Synergen Inc., the research assessed crucial parameters including growth performance, digestibility, innate immunity, antioxidant capacity, and resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus, a notorious shrimp pathogen.
Experimental Design
To carry out the study effectively, three replicate groups of 30 Pacific white shrimp, each with an initial body weight of 0.40 ± 0.001 g, were randomly assigned to 18 acrylic tanks (240 L) and fed one of the designated diets for a period of 53 days.
This rigorous experimental setup allowed for a comprehensive evaluation of the effects of Achyranthes aspera extract on shrimp health and performance.
Improved Growth Performance
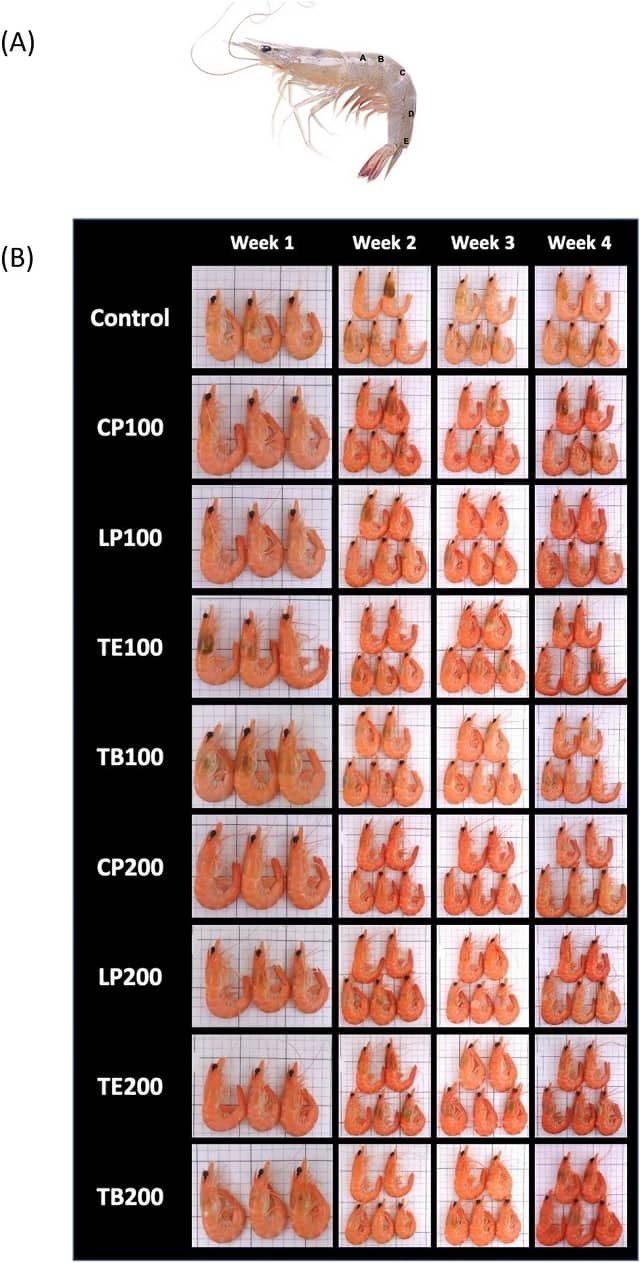
According to the study’s results, growth performance tended to improve with increasing levels of Achyranthes aspera extract in the diet.
Diets fed to shrimp with phytosterol concentrations of P20 and P80 showed significantly better growth performance compared to those with the control diet (Con) and the P10 diet.
This finding underscores the potential of Achyranthes aspera extract to boost shrimp growth, a key consideration for aquaculture operations seeking to maximize performance.
Enhanced Immune Response
Dietary phytosterol supplementation led to an improvement in the shrimp’s non-specific immune response. This is a critical aspect of disease prevention in aquaculture, highlighting the extract’s role in reinforcing the innate immunity of Pacific white shrimp.
Stay Always Informed
Join our communities to instantly receive the most important news, reports, and analysis from the aquaculture industry.
Improved Antioxidant Capacity
The study revealed that phytosterol supplementation contributed to an increased antioxidant capacity in shrimp. This is a particularly important finding, as antioxidants play a vital role in protecting cells from oxidative stress, promoting overall shrimp health.
Enhanced Digestibility
Achyranthes aspera extract had a positive impact on the apparent digestibility coefficients of dry matter and protein in shrimp diets. Improved digestibility contributes to efficient nutrient utilization, which is pivotal for both growth and overall health.
Disease Resistance
One of the most significant discoveries was the notable enhancement of shrimp disease resistance against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Shrimp fed the P20 diet exhibited superior resistance to this pathogen, an invaluable attribute in disease-prone aquaculture environments.
“In the present study, it was found that phytosterol supplementation (0.05–0.8 mg/kg) increases the innate immunity and antioxidant activity of shrimp, leading to reduced mortality and improved disease resistance against V. parahaemolyticus,” the researchers reported.
Conclusion
With its potential to improve growth, stimulate immunity, enhance antioxidant capacity, and increase disease resistance, Achyranthes aspera extract emerges as a promising functional feed additive.
The study’s findings suggest that the optimal dietary inclusion level of phytosterol from Achyranthes aspera extract falls within the range of 0.2 to 0.4 mg/kg, offering a practical guideline for shrimp nutritionists and farmers looking to optimize their operations and contribute to the sustainable growth of the aquaculture industry.
“Optimal supplementary level of A. aspera extract (200 mg/kg of phytosterol) in P. vannamei feed is expected to be 1–2 g/kg,” the researchers concluded.
Contact
Kyeong-Jun Lee
Department of Marine Life Science
Jeju National University
Jeju 63243, South Korea.
Email: kjlee@jejunu.ac.kr
Reference (Open Access)
Ko, D., Medagoda, N., Yun, K.-S., & Lee, K.-J. (2023). Effects of dietary supplementation of Achyranthes aspera extract on growth performance, digestibility, innate immunity, antioxidant capacity, and disease resistance of juvenile Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/jwas.13021
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.