Shrimp, a staple food in many cuisines worldwide, has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its rich lipid composition and potential health benefits. As a valuable source of bioactive molecules, shrimp has been found to possess anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antithrombotic properties, making it an attractive solution for the prevention and treatment of various chronic diseases.
A scientific review published by researchers from the Democritus University of Thrace and the Fisheries Research Institute delves into the lipid composition of various shrimp species, focusing on the potential health benefits of their bioactive compounds. The study, published in MDPI’s Marine Drugs journal, explains how these lipids can contribute to the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.
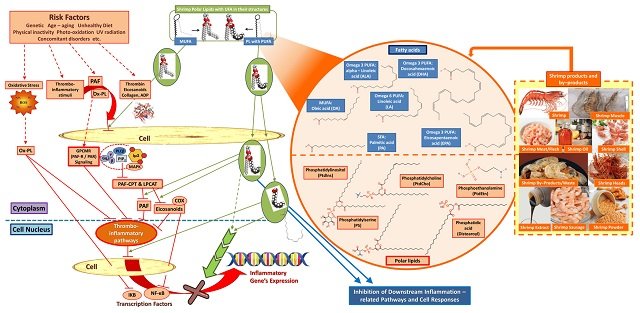
The Importance of Lipids in Shrimp
Lipids, a crucial group of biomolecules, play a vital role in our overall well-being. They serve as energy sources, precursors for synthesizing lipophilic vitamins, and key players in energy storage, signaling, and enzymatic activity. Shrimp, in particular, is rich in fatty acids, phospholipids, monounsaturated fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and saturated fatty acids, making it an excellent source of essential nutrients.
The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Shrimp
Shrimp is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), which are essential for cardiovascular health. These fatty acids have been shown to improve vascular health, reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and combat oxidative stress, making them integral to a healthy and nutritious diet.
Astaxanthin: A Powerful Antioxidant
Astaxanthin, a xanthophyll carotenoid, is a potent antioxidant found in shrimp. With remarkably high antioxidant activity, astaxanthin has demonstrated anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties, making it a valuable component of shrimp extracts.
Key Findings
The study provides an in-depth analysis of the nutritional value and bioactive characteristics of shrimp and its byproducts, highlighting its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antithrombotic, antitumor, antidiabetic, and other health-promoting properties. Key findings include:
- Shrimp is rich in bioactives, including n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), phospholipids (PLs), carotenoids, and phenolic compounds.
- Shrimp extracts have demonstrated positive effects on human health in numerous in vitro, in vivo, and randomized controlled studies. These effects include reducing inflammation, protecting against oxidative stress, and supporting cardiovascular health.
- Lipids from shrimp tails and byproducts can be applied in various industries, including food (as fish feed additives or natural flavor enhancers), pharmaceuticals (as drug formulation additives), nutraceuticals (as n-3 complementary diets), and cosmeceuticals (as skincare products).
- Lipid composition in shrimp varies by species and is influenced by endogenous and exogenous factors, such as sex, habitat, diet, and farming and processing methods.
- Extraction and cooking methods also affect shrimp lipid composition. Polar solvents like ethanol are more effective in extracting polar components, including phospholipids, while n-hexane is better for saturated fats. Cooking can alter the concentrations of certain fat types.
Health Benefits of Shrimp Consumption
According to the study’s results, the primary health benefits of shrimp consumption include:
- Cardiovascular Health: Shrimp’s rich omega-3 fatty acid content contributes to improved cardiovascular health by reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other heart-related conditions.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The anti-inflammatory properties of shrimp lipids may help alleviate chronic inflammation, a key factor in developing many chronic diseases.
- Antioxidant Activity: Antioxidants like astaxanthin help protect cells from oxidative stress, which can contribute to chronic disease development.
- Antithrombotic Effects: Shrimp lipids may help prevent blood clot formation, reducing the risk of thrombosis.
- Cancer Prevention: Some studies suggest that shrimp lipids may have anticancer properties, though further research is needed.
- Neurological Health: Omega-3 fatty acids, abundant in shrimp, are essential for brain function and may play a role in preventing neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Future Directions
While shrimp offers numerous health benefits, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action of its bioactive compounds and to valorize shrimp byproducts. Additionally, exploring ways to optimize shrimp aquaculture practices and minimize waste during processing will be crucial to maximizing the sustainability and economic viability of this valuable seafood.
Conclusion
Shrimp represents a valuable source of essential nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. These bioactive compounds offer a variety of health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health, reduced inflammation, and enhanced immune function. As research continues to uncover the full spectrum of shrimp’s health benefits, it is likely to become an even more integral part of a healthy and sustainable diet.
Stay Always Informed
Join our communities to instantly receive the most important news, reports, and analysis from the aquaculture industry.
Reference (open access)
Cholidis, P., Kranas, D., Chira, A., Galouni, E. A., Adamantidi, T., Anastasiadou, C., & Tsoupras, A. (2024). Shrimp Lipid Bioactives with Anti-Inflammatory, Antithrombotic, and Antioxidant Health-Promoting Properties for Cardio-Protection. Marine Drugs, 22(12), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22120554
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.







