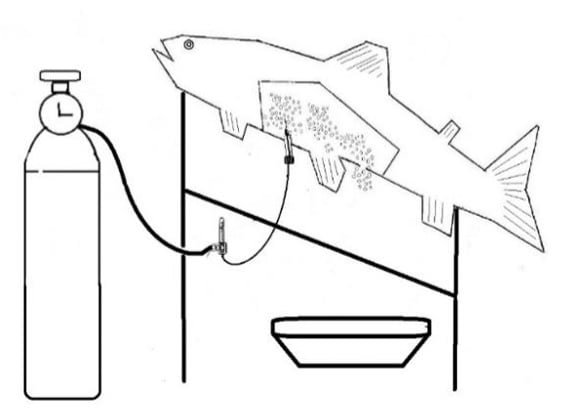
As aquaculture experts, we are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency and animal welfare in fish breeding. A key area is the collection of eggs from broodstock. The traditional technique involves a manual method where the fish’s abdomen is gently massaged to release the eggs. While effective, this method can be stressful for the fish and potentially damage egg quality.
A recent study by a researcher from the Shahid Motahary Cold Water Fishes Genetic and Breeding Research Center of the Iranian Fisheries Science Research Institute (IFSRI), published in the Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences, examined a promising alternative: pneumatic egg extraction. This method involves injecting gas at controlled pressure into the fish’s abdominal cavity, facilitating the release of eggs.
The researchers compared pneumatic extraction with the manual stripping method in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). They evaluated the impact on the quality of the collected eggs, relative fertility, extraction duration, and pH of ovarian fluids.
The challenge of egg quality
In animal breeding, high-quality eggs and sperm are crucial for maintaining the life cycle and ensuring the future of fish populations in aquaculture. Since breeding broodstock incurs significant costs, any fluctuation in the quantity or quality of gametes can significantly affect the competitiveness and sustainability of fish farms. Efficient methods to produce high-quality gametes are thus essential for the economic success of aquaculture.
The manual method is the primary approach traditionally used in fish farms for egg extraction. This technique involves securely holding the fish and applying gentle pressure to its abdomen, causing the release of eggs. While effective, it has limitations:
- Risk of internal injuries: Excessive pressure can damage the fish’s internal organs, such as the spleen and liver.
- Incomplete egg collection: Stopping before all eggs are released can cause egg breakage and a drop in the ovarian fluid pH due to yolk sac leakage, negatively impacting fertilization.
Pneumatic extraction: a promising alternative
The pneumatic extraction method offers a compelling alternative to the traditional manual approach. This technique involves injecting gas (often oxygen or nitrogen) into the female’s abdominal cavity, causing the eggs to be gently expelled by the gas pressure. First used in Australia in 1957, this method has shown promise in various fish species, including rainbow trout.
Among the main advantages of the pneumatic extraction method are:
- Improved egg quality and fertilization rates: Studies suggest that pneumatic extraction leads to higher fertilization percentages, better-quality eggs, and better egg survival rates.
- Reduced fish stress: The gentler nature of pneumatic extraction minimizes damage to the fish’s skin and mucus, promoting better fish welfare.
- Faster collection time: Research indicates that pneumatic extraction can be faster than manual methods.
Manual extraction vs. pneumatic extraction
The study analyzed the effects of both techniques on egg quality, relative fertility, extraction time, and the pH of ovarian fluids. The results showed that pneumatic extraction offers several advantages:
- Higher egg quality: Pneumatic extraction produces better-quality eggs with higher hatch rates compared to the manual method.
- Shorter extraction time: The pneumatic extraction process is quicker, taking only 39.5 seconds on average, compared to 42 seconds for the manual method.
- Lower impact on fish: Injecting gas at a controlled flow (1.5 L min-1) prevents the mortality of broodstock trout after extraction.
- Effectiveness and repeatability: Pneumatic extraction proves to be a more efficient technique with more consistent results.
Conclusion
“In general, pneumatic egg extraction produces higher-quality eggs with a higher hatch rate compared to the manual method,” the researcher concluded. He also recommends that the optimal conditions for this method include adjusting the gas flow to 1.5 L min-1, maintaining a gas pressure of 0.8 bar, and using a needle with a thickness ranging from 0.8 to 1.2 mm.
Stay Always Informed
Join our communities to instantly receive the most important news, reports, and analysis from the aquaculture industry.
Based on the study results, pneumatic egg extraction emerges as an innovative technique with the potential to transform rainbow trout breeding. Its implementation in fish farming could yield better-quality eggs, optimize working times, and, most importantly, ensure the welfare of broodstock fish.
Contact
Roghaye Mahmodi
Email: roghaye.mahmodi@gmail.com
Reference (open access)
Mahmoudi R. A comparative analysis of air and manual stripping techniques in female rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) broodstocks. IJFS 2024; 23 (4) :623-632 URL: http://jifro.ir/article-1-5384-en.html
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.







