Edwardsiellosis disease caused by Edwardsiella tarda generates significant economic losses in aquaculture farms worldwide. This disease can affect a wide range of hosts, including freshwater, brackish water, and marine aquatic animals.
Currently, antibiotics have become the main treatment for Edwardsiellosis in aquaculture species. However, the excessive use of antibiotics has led to an increase in cases of microbial resistance.
In this regard, there is a need to find alternative antimicrobial agents to control Edwardsiellosis in aquaculture, in order to reduce excessive reliance on chemicals and antibiotics.
A team of researchers from INTI International University, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, Universiti Malaysia Terengganu, Sylhet Agricultural University, among other academic institutions, published a scientific review describing the impact of Edwardsiellosis in aquaculture and highlighting the application of phytobiotics and the status of vaccines to combat this disease.
Phytobiotics and their bioactive compounds
Phytobiotics are plant-derived substances that have beneficial effects on organisms. Bioactive compounds such as alkaloids, carotenoids, and phenols are responsible for the biological activities of phytobiotics.
The biological activities of phytobiotics can be anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, among others.
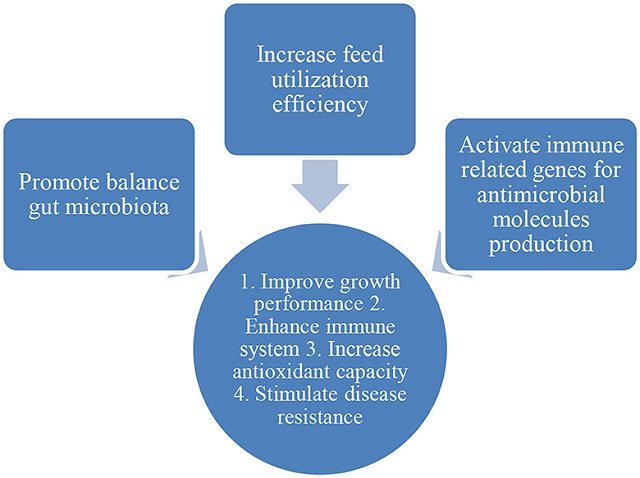
Generally, phytobiotics play an important role in promoting the growth of intestinal microbiota, thereby increasing feeding efficiency and activating genes related to immunity.
Impact of Edwardsiellosis in aquaculture
Edwardsiella tarda is an important bacteria causing diseases in aquaculture. However, there are four other similar pathogenic bacteria under the genus Edwardsiella: E. anguillarum, Edwardsiella piscicida, Edwardsiella ictaluri, and Edwardsiella hoshinae.
The E. tarda bacteria is responsible for many outbreaks of Edwardsiellosis in aquaculture, affecting species such as crucian carp, herbivorous carp, Japanese eels, Japanese flounder, Chinook salmon, sturgeon, catfish, seahorses, crocodiles, turbot, among others.
Stay Always Informed
Join our communities to instantly receive the most important news, reports, and analysis from the aquaculture industry.
Symptoms of Edwardsiellosis in infected fish species include exophthalmia, hernia, damage to internal organs, loss of pigment, swollen anus, and enlarged kidney.
Other symptoms of the disease reported in scientific literature include ascites and inflammation of internal organs.
Application of phytobiotics in aquaculture
There are some phytobiotics that are approved for use in animal production by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), such as cottonseed meal and rice bran. However, both phytobiotics cannot be applied beyond 20% in feed formulations.
The potential of phytobiotics, such as essential oils, plant leaves, flowers, and extracts, has been widely documented in scientific literature.
Phytobiotics can be used as feed additives in aquaculture, and some have been employed as a solution or medication through bath treatments.
Based on the mode of action of phytobiotics, their beneficial effects in aquaculture species include enhanced immune system, increased antioxidant activity, improved growth performance, and disease resistance stimulation.
β-Glucan
β-Glucan is a commercial polysaccharide that can be used as an immunostimulant.
Many studies have revealed that β-glucan can enhance the immune system in aquatic animals such as Oreochromis niloticus, Litopenaeus vannamei, Oncorhynchus mykiss, Lutjanus peru, Cyprinus carpio, and Trachinotus ovatus.
Microalga Nannochloropsis oculata
Several studies have highlighted the potential of the microalga Nannochloropsis oculata as a phytobiotic. It was found that N. oculata in the diet at a dose of 5% to 15% promotes growth and health status in Nile tilapia, O. niloticus.
Microalgae are widely used in aquaculture as they are rich in essential amino acids. Additionally, they also contain bioactive compounds such as essential vitamins and polysaccharides that can strengthen health status and promote growth.
Oregano oil
It has been reported that the essential oil of Origanum vulgare in the diet at a dose of 0.5% to 1% alleviates oxidative stress due to the presence of the insecticide cypermethrin in common carp, C. carpio.
The bioactive compounds present in the essential oil, such as carvacrol, thymol, cymene, and terpinene, are capable of increasing the antioxidant capacity of fish.
Conclusions
“Phytobiotics can be an alternative option for aquaculturists as a prophylactic agent against Edwardsiellosis. Currently, phytobiotics have high potential in controlling this disease,” conclude the authors of the study.
However, they emphasize the need for further research to investigate the effectiveness of phytobiotics against Edwardsiellosis in major aquaculture species such as eels, flounder, turbot, and channel catfish.
The study has been funded by the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia, and the Sustainable Agriculture Systems funds from USDA-NIFA.
Reference (open access)
Goh KW, Abdul Kari Z, Wee W, Zakaria NNA, Rahman MM, Kabir MA, Abdul Hamid NK, Tahiluddin AB, Kamarudin AS, Téllez–Isaías G and Wei LS (2023) Exploring the roles of phytobiotics in relieving the impacts of Edwardsiella tarda infection on fish: a mini-review. Front. Vet. Sci. 10:1149514. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1149514
Editor at the digital magazine AquaHoy. He holds a degree in Aquaculture Biology from the National University of Santa (UNS) and a Master’s degree in Science and Innovation Management from the Polytechnic University of Valencia, with postgraduate diplomas in Business Innovation and Innovation Management. He possesses extensive experience in the aquaculture and fisheries sector, having led the Fisheries Innovation Unit of the National Program for Innovation in Fisheries and Aquaculture (PNIPA). He has served as a senior consultant in technology watch, an innovation project formulator and advisor, and a lecturer at UNS. He is a member of the Peruvian College of Biologists and was recognized by the World Aquaculture Society (WAS) in 2016 for his contribution to aquaculture.







